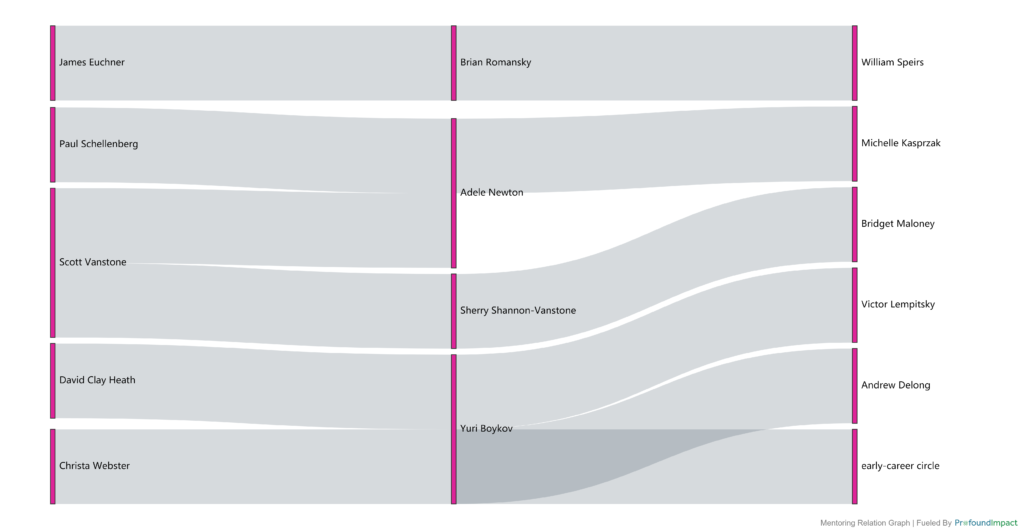
Adele Newton

Strategic Partnerships Pioneer and Mentor
The Impact of Making Connections and Fostering Mentorship
As the oldest of five children, including three younger sisters, being a mentor to young women and a leader is something that has always come naturally to Adele Newton. Over the course of her career, she has wanted to provide others with the guidance and support she didn’t always have.
“I had very few female mentors – but those I did have made a big difference to how I looked at progress in my career,” says Adele. “I know I would have been more confident and taken more risks if there had been more women role models for me. So if I can make the road a little easier and more visible to a young woman, that means a lot to me and to her.”
Creating her own way
When Adele started her BMath at the University of Waterloo, she expected to have a fairly straightforward career path as a teacher. She realized teaching was not what she had hoped for. Instead she created her own way, and after working in a series of positions at the university, she found her calling.
“When I managed the President’s Club program for the University of Waterloo, I learned a lot about the importance of giving back to the university and the difference it makes to the institution. It was when I first understood the potential for connecting industry to the research part of the university and how that could benefit both parties.”
Over the years, Adele has facilitated relationships between industry and academia, which has led to countless research collaborations as well as valuable opportunities for students. Canadian companies, such as Alias Research, Side Effects Software, Bell Canada, and BlackBerry all benefited from connections Adele helped them make with universities around the world.
The value of mentorship
Her talent for creating connections has allowed Adele to pursue her passion for outreach and mentoring others. While working in the computer graphics industry, she became involved with SIGGRAPH, the world’s largest conference in computer graphics. Adele saw an opportunity to create programs to introduce children and teenagers to the field. She recognized the important role women play in mentoring others.
“I have almost always been the only or one of the few women in the room during my career. That’s just the nature of tech – though it is changing. When I suggested we have an outreach program for SIGGRAPH, I knew that most of the mentors would be male – but we had some wonderful women participate. I saw the kids’ eyes light up. These were kids where 10-14 years old from inner city schools in New Orleans. I knew we had sparked ideas and possibilities in them. It was very powerful, and I knew I wanted to keep doing this.”
In more recent years, Adele co-founded LAUNCH Waterloo – an organization that aims to introduce children to science, technology, engineering, arts, and math through fun recreational programs. She is also a mentor in the Women in Communication and Technology (WCT) Waterloo Region Mentorship Circles, a program that connects women with mentors.
“Mentoring younger women is a joy! I love sharing my experience and being there for them to run their ideas by me and to provide insight that they may not have had otherwise.”
A career filled with accomplishments
As Adele begins to consider retirement and focus on travel, writing and her love (and exceptional talent) for creating mouthwatering culinary creations, she can look back with pride on her accomplishments. She has influenced countless individuals – men and women alike – through her mentorship and guidance. Many of the research partnerships she facilitated continue thanks to the connections she originally created.
“I look back on my schooling and my career and am proud of the work I did with industry and universities and the lasting effect those programs have had. There are still research collaborations in place that started as a result of some of those programs. I know my work provided motivation and funds for students of all ages (from grade school to grad school) to go to school when they might not otherwise have thought to or been able to.”
Adele has been a valuable contributor to Profound Impact and will continue to work on special projects on occasion. While we are sorry to see her go, we are happy she will be able to indulge in her love of cooking and travel, and wish her all the best in retirement.