CEO Message

Profound Impact is continuing to work with eVision Inc. to finalize the details of our partnership, which will embody our joint vision to disrupt the US $2.5 trillion annual Research Tech industry by offering the first-ever AI-enabled end-to-end Research Grant Management solution. Canadian technology is taking the lead on the global stage to transform end-to-end Research Grant Management while creating an AI-enabled grant system that matches workflow and compliance effectively.
Profound Impact is also proud to partner with Vector Institute’s FastLane program as a member, along with an amazing group of like-minded innovators. FastLane enables Canadian start-ups to accelerate their AI commercialization journey and compete more effectively in the global economy. You can learn more about the FastLane program and what Vector Institute has to offer here.
The Profound Impact team has been busy with presentations on the use of AI to strengthen technical communities and uncover innovative ways to align people with opportunities. Last month, I was a guest on The Smart Connector’s livestream to discuss the intersection of AI and funding and to provide insights into innovative funding strategies and the latest technological advancements. You can hear my conversation with Jane Bayler at AI for Impact: Transforming Research Funding with Technology.
Brian Romansky, Profound Impact’s Chief Strategic Advisor, led a session on effective policy-compliant AI use cases for research administrators at the National Council of University Research Administrators (NCURA) conference in Washington, DC on August 6th.
The Profound Impact team is working on plans for the 5th Profound Impact Day, a time to commemorate the world’s innovative researchers and changemakers who are leaving their mark on the global community through their research, innovation, and impact. As the proud sponsor of the CS-Can|Info-Can Outstanding Early Career Computer Science Researcher Award, we will celebrate on September 16th by honoring the award nominees and three award winners. Dr. Feridun Hamdullahpur, the former President and Vice-Chancellor of the University of Waterloo, will lead a virtual fireside chat with Professor Ali Ouni and Professor Liam Paull, two of the award winners. Register to attend this free event here!
On September 17, at 12:00 – 1:00 p.m. EST, Brian Romansky will review how AI technology stands poised to revolutionize the research funding ecosystem at a webinar presented by CARA, the Canadian Association of Research Administrators. You can get more information and register to attend the webinar here.
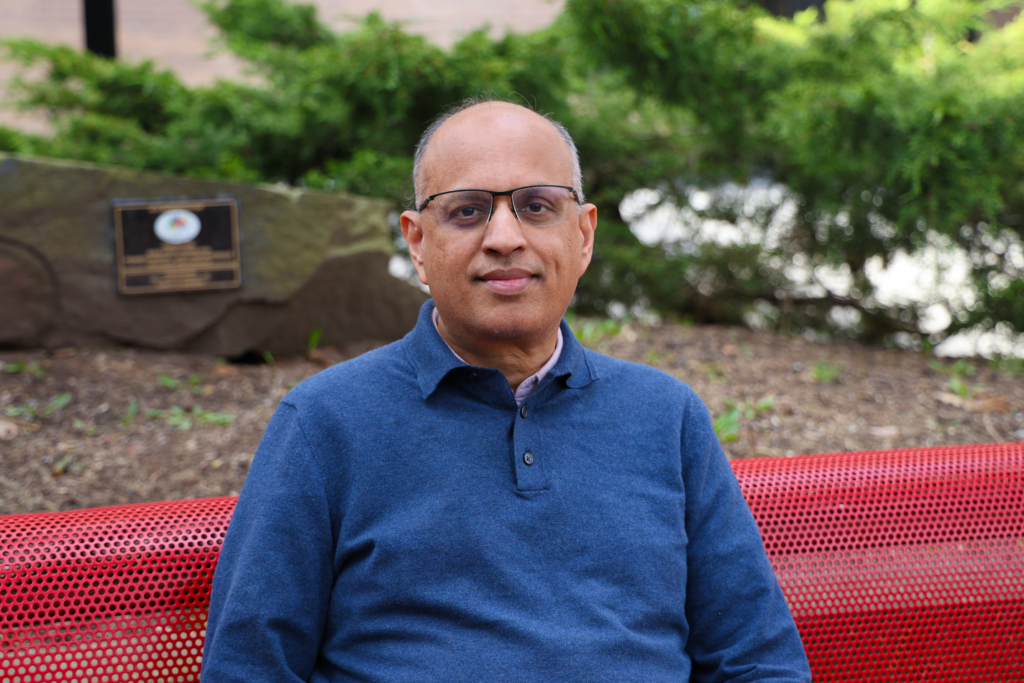
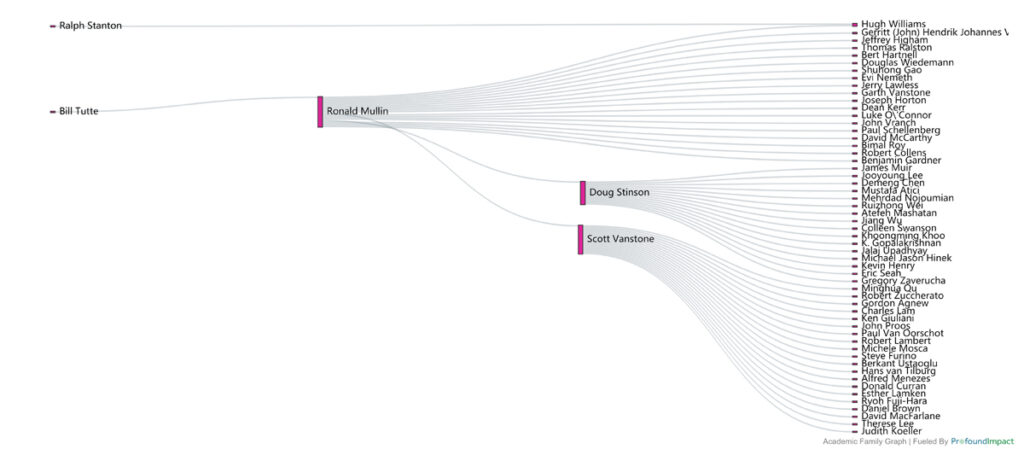
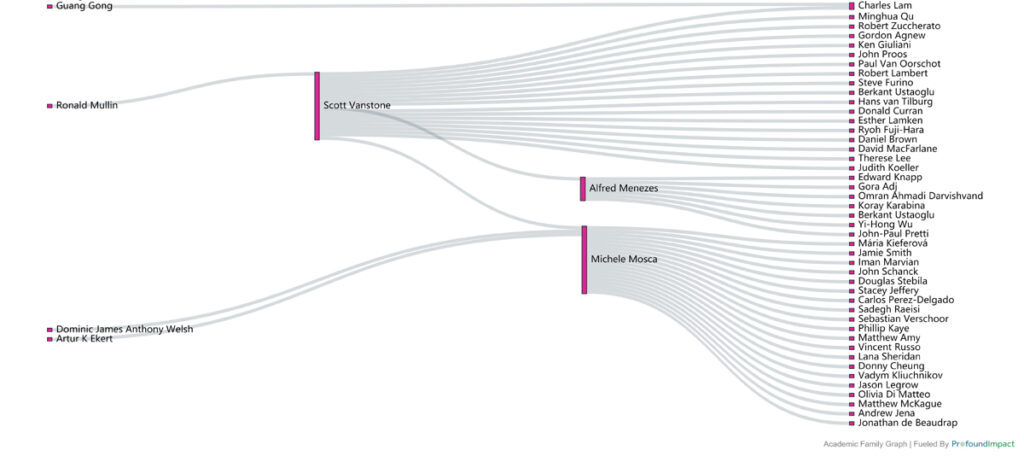
In this month’s issue of Profound Connections, you’ll meet Lisa Lambert, CEO of Quantum Industry Canada. Lisa is a versatile and dynamic leader and mentor who has dedicated her career to driving innovation, execution, and business growth in high-velocity, ever-evolving environments. And you’ll learn about Alfred Menezes’ career as a world-renowned cryptography researcher, industry advisor, outstanding teacher, and YouTube content creator in this month’s Researcher Spotlight.
As always, thank you for your support and we hope you enjoy this month’s edition of Profound Connections!
Sherry Shannon-Vanstone